- Introduction
- How Signal Generators Work
- Applications of Signal Generators
- Types of Signal Generators
- RF Signal Generators
- Vector Signal Generators
- Arbitrary Waveform Generators
- Function Generators
- Pulse Generators
- Signal Generators – Key Features
- Choosing the Right Signal Generator
- Invest in a Like New Signal Generator With Our Reliable Refurbished Options
- Best Deals on Signal Generators
- Closing Thoughts From Keysight
- Whenever You’re Ready, Here Are 4 Ways We Can Help You
As an engineer, you know how important accurate and reliable testing is in ensuring the quality and performance of your designs. But with an overwhelming number of signal generators on the market, finding the right one can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack.
That's why it's so important to understand the various features and capabilities of signal generators, so you can make an informed decision that meets the unique needs of your projects and tests. The right signal generator can make all the difference in getting the data you need to refine and improve your designs, while a poor choice can lead to a time-consuming and costly rework.
A signal generator is an electronic device that generates repeating or non-repeating waveforms used to test and evaluate electronic test equipment. It simulates real-world signals and conditions, enabling you and other engineers to test the performance and behavior of electronic systems.
You find signal generators in different fields, including telecommunications, audio engineering, and medical electronics.
The history of signal generators dates back to the 1920s when they were first developed as simple sine wave generators. Over time, they have evolved to include more complex waveform generation capabilities, improved accuracy, and greater flexibility.
Today, signal generators offer a wide range of output waveforms, modulation options, and frequency ranges, allowing you to tailor your test signals precisely to your specific needs.
How Signal Generators Work
A signal generator has several key components, including an oscillator, modulator, amplifier, and output stage. The signal generation process starts with the oscillator, which generates a stable and repetitive waveform, such as a sine wave.
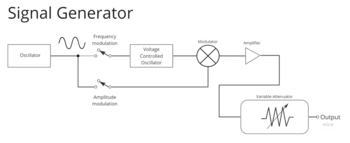
The waveform passes through the modulator, which shapes the waveform into the desired signal type, such as a square wave or triangle wave. It adds any modulation, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase modulation. It then amplifies the output signal to the desired level and sends it to the DUT (device under test).
A signal generator can generate various waveforms, including sine, square, triangle, sawtooth, and arbitrary. Sine wave signals are commonly used for testing and evaluating audio systems, while square and triangle signals test digital circuits. Sawtooth and arbitrary signals test various electronic systems, as they can simulate real-world signals and conditions.
While signal generators are handy tools, they also have limitations and challenges.
- Accuracy. One of the biggest challenges is accuracy, as even minor errors in the generated signal can affect the test results.
- Noise. Another challenge is noise, which can corrupt the signal and limit its usefulness.
- Distortion. A final issue that can also be a problem is distortion, which can introduce unwanted non-linearities into the signal.
To overcome these challenges, choose the correct signal generator for the application and use it correctly, considering its specifications and limitations.
Applications of Signal Generators
You use signal generators in various industries and applications, testing and measuring equipment ranging from electronic equipment to telecommunications and audio/video equipment. Let's take a closer look at some of the most common applications.
| Industry | Industry |
|---|---|
| Electronic testing | Signal generators are essential for engineers, as they allow for precise and customizable signals to test and evaluate electronic systems. For example, engineers can use signal generators to simulate real-world signals and conditions. |
| Telecommunications | Signal generators test and verify the performance of various communication systems, such as cellular networks, satellite systems, and data networks. For example, a technician can use a signal generator to transmit a test signal to a cellular base station to evaluate its receiver sensitivity, transmitter power, and other performance metrics. |
| Audio and video | Signal generators test and evaluate audio and video equipment, such as amplifiers, speakers, and displays. For example, signal generators generate sine wave signals to test the frequency response of audio systems. |
| Automotive | Signal generators test and evaluate various automotive electronic systems, such as engine management systems, powertrain control systems, and infotainment systems. For example, a signal generator can simulate sensor signals, such as throttle position and engine speed, to test the performance of engine management systems. |
As you can see, signal generators are versatile and valuable tools for engineers and technicians, providing a range of signals for testing and evaluating electronic systems in various industries and applications. Whether you're working in telecommunications, audio and video equipment, or the automotive industry, a signal generator can help you achieve accurate and reliable testing results.
Types of Signal Generators
There are many signal generators available on the market, from simple function generators to complex arbitrary waveform generators. Let's take a look at five common types of signal generators.
- RF signal generators
- Vector signal generators
- Arbitrary waveform generators
- Function generators
- Pulse generators
RF Signal Generators
A radio frequency (RF) generator generates high-frequency signals in the radio frequency spectrum, typically ranging from a few kilohertz to several gigahertz. RF generators can test and evaluate the performance of RF components and systems, such as antennas, filters, amplifiers, and communication systems.
The primary function of an RF generator is to provide a stable and reliable signal source for testing and evaluating electronic circuits and devices. RF generators consist of a local oscillator, a modulator, and a power amplifier.
- The local oscillator generates the basic RF signal.
- The modulator adds the desired modulation to the signal, such as amplitude modulation (AM) or frequency modulation (FM).
- The power amplifier amplifies the modulated signal to the desired level, making it suitable for testing and evaluating RF components and systems.
You can find RF generators in various applications, such as telecommunications, military and defense, and industrial electronics. They play a big role in testing and evaluating RF components and systems, ensuring they meet the desired performance specifications.
Vector Signal Generators
A vector signal generator (VSG) is a signal generator that can generate both amplitude and phase-modulated signals, also known as vector signals. Unlike traditional signal generators, which only generate signals with a constant amplitude, a VSG can generate signals with variable amplitude and phase, which are essential for testing and evaluating cellular networks and satellite systems.
The primary function of a VSG is to generate complex signals for testing and evaluating communication systems and electronic devices, such as filters, amplifiers, and modems.
A VSG typically includes a digital signal generator, a modulator, and a power amplifier, that work together to produce the desired signal. The digital signal generator generates a baseband signal, which is then modulated in amplitude and phase to make the final modulated signal.
You can find VSGs in the telecommunications industry, where they play a critical role in testing and evaluating modern communication systems and devices. In other industries, such as military and defense, VSGs test and evaluate radar and missile guidance systems.
Arbitrary Waveform Generators
An arbitrary waveform generator (AWG) is a signal generator that can produce any waveform within its frequency range. Unlike other signal generators that generate predefined waveforms, such as sine, square, and triangle waves, an AWG can produce a wide range of waveforms that can be programmed or defined by the user.
The waveform is created by digitally synthesizing a series of samples stored in memory, which are then converted to an analog signal by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
You find AWGs in various applications, such as
- Electronic testing and measurements
- Telecommunications
- Audio and video equipment
- The automotive industry
- Military and defense
- Research and development
AWGs offer high precision, flexibility, and versatility, allowing you to generate different waveforms for testing and evaluation purposes. Additionally, an arbitrary waveform generator can generate more sophisticated waveforms, such as pulsed and modulated signals, that can simulate real-world conditions, making them an essential tool in many industries.
Function Generators
A function generator generates various electrical waveforms, such as sine, square, triangle, and sawtooth, over a wide range of frequencies. The main function of a function generator is to provide a convenient and versatile source of signals for testing and evaluating electronic circuits and devices.
Function generators typically consist of a waveform generator, a frequency control circuit, and an amplifier. The waveform generator generates the basic waveform, while the frequency control circuit determines the frequency of the waveform. The amplifier amplifies the waveform to the desired level, making it suitable for testing and evaluating electronic circuits and devices.
You will find function generators in various applications, such as electronics testing, education, and research. Electronics engineers, technicians, and students use function generators to test and evaluate the performance of electronic circuits and devices. They are also used in the development and testing of audio and video equipment, as well as in the production of various electronic devices.
Pulse Generators
A pulse generator generates electrical signals or pulses, typically with precise timing and duration. Pulse generators test and evaluate various electronic circuits and devices, such as digital circuits, timing circuits, and communication systems.
The primary function of a pulse generator is to provide a precise and controlled source of pulses for testing and evaluating electronic circuits and devices. Pulse generators consist of a timing circuit, a shaping circuit, and an amplifier.
The timing circuit determines the timing of the pulses, while the shaping circuit determines the shape of the pulses, such as square, triangular, or sawtooth. The amplifier amplifies the pulses to the desired level, making them suitable for testing and evaluating electronic circuits and devices.
Many people in different fields use pulse generators.
- Electronics engineers use pulse generators to test and evaluate the performance of digital circuits, timing circuits, and communication systems.
- Technicians use pulse generators to diagnose and repair electronic devices and systems.
- Researchers use pulse generators to study and experiment with electronic circuits and systems.
- Students in electronics and engineering courses use pulse generators to learn about and experiment with electronic circuits.
Signal Generators – Key Features
When choosing a signal generator, it is important to consider several key features to ensure that it will meet your needs and perform to your expectations. This way, you can be sure that your signal generator will provide accurate and reliable test results.
- The frequency range of a signal generator refers to the range of frequencies in hertz (Hz) that the generator can produce. The frequency range is essential to consider as it affects the accuracy of the generated signal and the ability to test different devices and systems.
- The amplitude range refers to the range of amplitudes that a signal generator can produce. The higher the amplitude range, the more versatile and accurate a signal generator is. It is important to consider the amplitude range to ensure that the generated signal has the desired amplitude level for the application.
- Output power refers to the level of power supply that a signal generator can produce. This is an essential factor to consider as it affects the accuracy and range of the generated signal. Too low or too high an output power can lead to inaccurate test results or poor performance of the device under test.
- Modulation capabilities refer to the ability of a signal generator to modulate the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the generated signal. Modulation is important as it allows you to test different devices and systems, including those that use amplitude modulation, pulse modulation, frequency modulation, or phase modulation.
- Sweep and burst functions allow the user to generate signals over a specified frequency range and time duration. This function is useful for testing devices and systems that require periodic signals, such as radio frequency transmitters.
- The format of a signal generator refers to the type of waveform that can be generated (e.g., sine, square, triangle, etc.). You will need to consider the format of a signal generator to ensure that it can create the type of signal required for your application.
- Triggering options allow the user to synchronize the generation of signals with other signals or events. This function is vital for testing systems that require synchronization, such as digital circuits and timing circuits. Triggering is also helpful for studying and experimenting with electronic circuits, as it allows you to control the timing of the generated signals.
- Waveform memory allows the user to store waveforms for later use. This function is useful for storing commonly used signals or waveshapes and can save time when setting up tests or experiments.
Choosing the Right Signal Generator
Before buying a signal generator, consider the intended application. Different applications have different requirements for frequency range, output power, modulation capabilities, and other features.
Here are some general recommendations for various applications.
- For general-purpose testing, it's best to have a signal generator with a wide frequency range and high output power. You should also consider modulation capabilities, such as amplitude modulation and frequency modulation, as well as sweep and burst functions to allow for testing periodic signals.
- For telecommunications applications, a signal generator with a high-frequency range and a low-noise floor is essential. This allows for accurate testing of the system, as well as the generation of signals with low levels of interference. You will also want to consider complex modulation formats used for telecommunications, such as frequency-shift keying and phase modulation.
- For testing audio and video equipment, you will want a signal generator with a low distortion level. Low distortion ensures that the signal generated is of high quality and without any distortion. It's also important to consider modulation capabilities such as amplitude-shift keying, frequency-shift keying, pulse code modulation, and quadrature modulation.
- For testing in the automotive industry, you will want a signal generator with a wide frequency range and high output power. Since auto electronics are often used in harsh environments, you will want to ensure your signal generator can generate signals with high levels of accuracy and reliability.
Invest in a Like New Signal Generator With Our Reliable Refurbished Options
If you're in the market for a signal generator, buying a used model is the more affordable and eco-friendly option. Remember, you don't have to sacrifice quality to get a good deal. A used signal generator from Keysight will get you an accurate, high-quality device at a fraction of the cost.
Keysight is the only supplier where you can get a calibrated, premium-used signal generator. What assurance does that give? It means you can trust the accuracy of your result. Our premium used signal generators have been through the same rigorous testing as our new equipment and come with the same one-year warranty!
So, if you want to buy a used signal generator without sacrificing quality, look no further than Keysight. Visit Keysight's Used Equipment Store today and browse our selection of Signal Generators.

Best Deals on Signal Generators
Closing Thoughts From Keysight
Signal generators play a crucial role in electronic testing in various industries. From sine and square signals to RF and vector signals, the right signal generator can greatly impact the success of an engineer's project.
Take the story of Dan, an engineer struggling with unreliable signal generators affecting his work and test accuracy. Dan found the solution in Keysight signal generators, which improved his work and test results without compromising on price or quality.
We know that engineers need reliable equipment to get the job done right. That's why our used signal generators are a great choice for anyone looking for cost-effective solutions without sacrificing accuracy and reliability. With our commitment to quality and innovation, you can trust that your signal generator needs will be met and exceeded.
Ready to purchase your used signal generator? Visit our Used Equipment Store today and find the perfect signal generator.

Whenever You’re Ready, Here Are 4 Ways We Can Help You
- Browse our Premium Used Signal Generator offers
- Call tech support US: 1 800 829-4444
Press #, then 2. Hours: 7am – 5pm MT, Mon– Fri - Talk to our sales support team by clicking the icon (bottom right corner) on every offer page
- Talk to your account manager for custom deals




























